If you’ve ever eaten sushi or Chinese takeout, you’ve probably tried fake crab meat at some point, even if you didn’t know it.
Imitation crab has become a popular ingredient in restaurants, grocery stores, and home kitchens because it can be used in many ways, is easy to prepare, and doesn’t cost a lot.
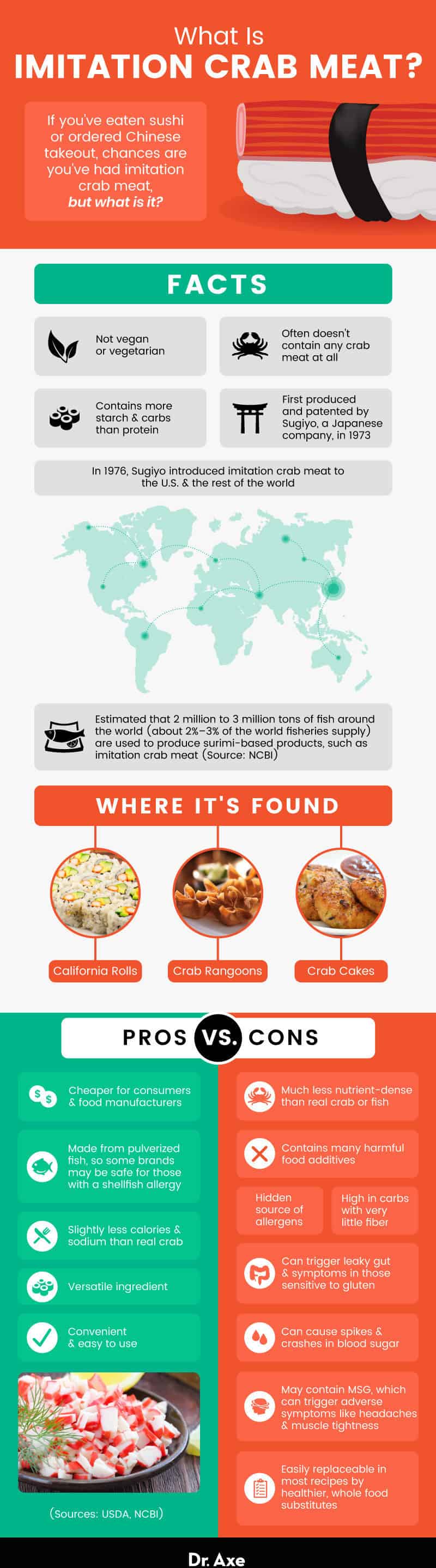
Is fake crab vegan? No, fake crab meat is not vegan or even vegetarian, despite what most people think. To make things even stranger, it usually doesn’t have any crab meat in it at all and has more starch and carbs than protein.
Here’s what’s really in your favorite sushi rolls and why you might want to think twice about ordering takeout. Ad.
Imitation crab meat sometimes called surimi, is a popular ingredient found in many dishes like California rolls crab rangoon, and crab cakes. However, this seafood product doesn’t actually contain much real crab – if any at all.
The main ingredient in imitation crab is fish, usually Alaska pollock This white fish is pulverized, mixed with fillers, and then molded to resemble the taste, texture, and appearance of real crab meat
With growing concerns over mercury in seafood, many people wonder: does imitation crab meat have mercury? Let’s take a closer look at this controversial ingredient.
The Link Between Fish and Mercury
Mercury is a heavy metal that is toxic to humans when consumed in high amounts. It can bioaccumulate in the ocean, so larger predatory fish near the top of the food chain tend to have higher mercury levels.
Consuming too much mercury during pregnancy has been linked to potential developmental problems in babies. That’s why the FDA recommends pregnant women avoid high mercury fish like tilefish, swordfish, shark, and king mackerel.
So where does imitation crab meat fall? Surprisingly, it tends to be low in mercury. Here’s why:
Why Imitation Crab is Low in Mercury
The key is understanding what fish is used to make imitation crab meat. Alaska pollock is the most common.
Pollock is a smaller white fish that is low on the food chain. Since it doesn’t eat lots of other contaminated fish, pollock tends to be very low in mercury. The FDA lists it as a “Best Choice” fish with barely detectable mercury levels.
Other white fish sometimes used in imitation crab also test low for mercury, like cod, hake, and haddock. Whiting or tilapia may be used too.
So while real crab can have varying amounts of mercury depending on the species, imitation crab made from fish like pollock contains hardly any mercury at all.
Federal Mercury Guidelines for Fish
The FDA and EPA have established recommendations for mercury levels in fish and shellfish. This helps consumers make educated choices, especially pregnant women.
-
Fish with the lowest mercury levels can be eaten 2-3 times per week. This includes salmon, pollock, tilapia, shrimp, catfish, cod, and canned light tuna.
-
Fish with low-to-moderate mercury can be eaten 1-2 times per week. Examples are crab, fresh tuna, haddock, trout, and Atlantic mackerel.
-
Fish with moderate-to-high mercury should only be eaten 1 time per month. These include Chilean sea bass, grouper, halibut, snapper, and albacore tuna.
-
High mercury fish like swordfish, shark, tilefish, and king mackerel should be avoided. These have the highest mercury levels.
Again, imitation crab made from fish like pollock falls into the lowest mercury category. Pregnant women can safely eat it a few times per week according to these federal guidelines.
Other Imitation Crab Ingredients
Beyond fish, imitation crab contains other concerning ingredients like additives and fillers. Here are a few to watch out for:
-
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) – This common flavor enhancer has been linked to headaches, numbness, muscle tightness and more in sensitive individuals. Some brands add MSG to imitation crab for a savory flavor.
-
Artificial Colors – Dyes like carmine, paprika extract and beet juice concentrate are sometimes added to give imitation crab a more vibrant color. Studies connect some artificial colors to hyperactivity in children and allergy-like symptoms.
-
Carrageenan – This additive extracted from red seaweed acts as a thickening agent in imitation crab. Degraded forms of carrageenan may cause gastrointestinal issues like bloating and inflammation.
-
Phosphates – Additives like sodium tripolyphosphate improve moisture retention in imitation crab. High phosphate intake has been linked to an increased risk of kidney damage.
Whenever possible, choose additive-free brands of imitation crab. Read ingredient lists closely since contents can vary widely between products.
Healthier Alternatives to Imitation Crab
If you want to avoid the additives found in imitation crab, what are some alternatives? Here are a few healthier options:
-
Real Crab – Get the nutritional benefits of crab meat without imitation versions. Go for sustainably caught Alaskan king, snow or Dungeness crab when possible.
-
Shrimp – Cooked shrimp offer protein, vitamin B12 and iron similar to crab. Opt for wild caught or sustainably farmed shrimp.
-
Lobster – High in protein and low in mercury, lobster makes a delicious special occasion swap for imitation crab.
-
Canned Salmon – Look for wild Alaskan salmon canned with bones for an inexpensive, high protein and low mercury alternative.
-
Tuna – For a budget friendly choice, try mercury-free canned light tuna as a replacement in seafood salads or sandwiches.
-
Turkey or Chicken – Deli meats like all natural oven roasted turkey or chicken breast have a similar flaky texture to imitation crab.
The Bottom Line
So does imitation crab meat have mercury? While real crab can contain varying amounts, imitation crab made from fish like pollock is very low in mercury.
Pregnant women can safely eat small amounts of imitation crab a few times per week based on federal seafood guidelines. Just beware of the additives and fillers used like MSG, carrageenan and artificial colors.
Whenever possible, choose brands without these concerning ingredients or try healthier alternatives like shrimp, canned salmon or turkey. This allows you to skip the seafood imposter and get more authentic nutrition from your meal.
:strip_icc()/Imitation-Crab-by-MarkGillowGetty-Images-2000-6c833061640844b0bc418c2f39a6ecd7.jpg)
Imitation Crab vs. Real Crab
Imitation crab nutrition is relatively low in calories but contains some protein, carbohydrates and sodium.
A three-ounce serving of imitation crab meat (about 85 grams) contains approximately:
- Calories: 80.8
- Total Carbohydrates: 12.8 g
- Fiber: 0.4 g
- Sugar: 5.3 g
- Total Fat: 0. 4 g Saturated Fat: 0. 2 g Polyunsaturated Fat: 0. 1 g Monounsaturated Fat: 0. 2 g Trans Fat: 0. 001 g .
- Protein: 6.5 g
- Sodium: 450 mg (20% DV*)
- Vitamin B12: 0.5 mcg (21% DV)
- Magnesium: 36.6 mg (9% DV)
*Daily Value: Percentages are based on a diet of 2,000 calories a day.
Compared to real crab, imitation crab is significantly lower in many nutrients, including protein, vitamin B12 and selenium. Crab also provides a much wider range of nutrition than imitation crab meat. Ad.
For comparison, a three-ounce serving of cooked queen crab (about 85 grams) provides approximately:
- Calories: 97.8
- Total Fat: 1. 3 g Saturated Fat: 0. 2 g Polyunsaturated Fat: 0. 5 g Monounsaturated Fat: 0. 3 g Trans Fat: 0 g .
- Protein: 20.1 g
- Sodium: 587 mg (26% DV*)
- Vitamin B12: 8.8 mcg (367% DV)
- Selenium: 37.7 mcg (69% DV)
- Copper: 0.5 mg (56% DV)
- Zinc: 3.1 mg (28% DV)
- Niacin: 2.5 mg (16% DV)
- Riboflavin: 0.2 mg (15% DV)
- Iron: 2.5 mg (14% DV)
- Magnesium: 53.6 mg (13% DV)
- Phosphorus: 109 mg (9% DV)
- Folate: 35.7 mcg (9% DV)
- Vitamin C: 6.1 mg (7% DV)
- Vitamin B6: 0.1 mg (6% DV)
*Daily Value: Percentages are based on a diet of 2,000 calories a day.
Along with the nutrients listed above, cooked crab also has thiamine, vitamin A, pantothenic acid, calcium, potassium, and manganese in it.
Imitation crab, also known as surimi, is a seafood product that is made by processing and flavoring fish. The ingredients commonly used in imitation crab include:
- Alaska Pollock (or another white fish): This is the main ingredient and what fake crab is made of.
- Water: Used to hydrate and mix the ingredients.
- Wheat Starch or Modified Tapioca Starch are added to make the surimi smoother and stick together better.
- Sugar: Adds sweetness to balance the flavors.
- Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol that is used to add sweetness and keep moisture in foods.
- Crab Flavoring: Artificial crab flavoring is often used to make food taste better and more like real crab.
- Cornstarch: Sometimes used as a thickening agent.
- Soybean oil is usually used because it has a lot of fat in it.
- Egg Whites: These can be added for texture and binding.
- Salt: For flavor enhancement.
- Natural and Artificial Flavorings: To get the right taste, different seasonings and flavorings are added.
- Sodium Tripolyphosphate: A common food additive used to retain moisture.
- One more ingredient that helps make the texture better is tetrasodium pyrophosphate.
It’s important to note that the exact ingredients may vary among different brands and products. Always check the product label for the most accurate information. Additionally, if you have allergies or dietary restrictions, it’s advisable to carefully read the ingredient list.
Many times, imitation crab has a lot of different ingredients added to it to make it taste better, make the texture better, and make it last longer. Here are some common additives found in imitation crab:
- Sodium Tripolyphosphate: Used as a preservative and to retain moisture.
- Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate is an ingredient in food that helps make it smoother and keep its moisture.
- Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol that helps keep moisture in food and makes it taste sweet.
- Sugar: Added for sweetness to balance flavors.
- Salt: Used for flavor enhancement.
- Multisodium Glutamate (MSG) is a flavor enhancer that gives food a savory or umami taste.
- Artificial crab flavoring is usually a mix of natural and artificial flavors that make food taste like real crab.
- Colorings: Some fake crab products may have colorings in them, like paprika extract or carmine, to make them look better.
- Binding Agents: Gums and binding agents like carrageenan and xantham gum are used to help the ingredients stick together.
Imitation crab is a popular choice among consumers and food manufacturers because it’s cheap to buy and make. So, is it good for you?
It’s also easier to use, more convenient, and easier to find than fresh crab meat. You can find it at most major stores across the country.
Plus, it’s very versatile. It goes well with salads, sushi rolls, and stuffed mushrooms. It’s also often used in recipes that call for fake crab meat, like dips, cakes, and pasta dishes.
Click on the link to see the fake crab nutrition facts. It has some advantages over real crab meat. Not only is each serving lower in imitation crab calories, but it’s also a bit lower in sodium.
Plus, most of it is made from ground fish like pollock, so some brands may be a safe alternative to crab meat for people who are allergic to shellfish.
The question is whether fake crab is healthy or just a “fake food” that could have harmful effects.
Nutritionally speaking, imitation crab is slightly lower in calories and sodium than fresh crab. However, it’s also lower in plenty of beneficial nutrients, such as protein, vitamin B12 and selenium.
Another difference is that real crab meat has a lot more types of nutrients and important vitamins and minerals in each serving.
Also, imitation crab is full of unhealthy ingredients that might cause problems like leaky gut and inflammation.
It can also be a hidden source of potential allergens like gluten. If you are sensitive to gluten or have celiac disease, eating gluten can make you feel tired, have diarrhea, and have abdominal pain.
Long term, eating even small amounts of gluten can cause increased intestinal permeability, or leaky gut, in those who are sensitive.
Other bad things like sugar, starch, and vegetable oils are added by manufacturers to help the finished product keep its shape. Because of these extra ingredients, fake crab has a lot more carbs than real crab meat. Each serving has about the same amount of carbs as a slice of white bread.
If you eat too much of it, your blood sugar will rise quickly and then drop again because it doesn’t have enough fiber to slow down the absorption of sugar.
Some brands also add in MSG to amp up the flavor of imitation crab meat. MSG is an ingredient that is added to savory foods to make them taste better. You can find it in a lot of Asian foods and processed foods.
However, many people are sensitive to MSG, reporting symptoms like headaches, muscle tightness, weakness and numbness/tingling after consumption. That’s partly why it’s often considered one of the worst ingredients around.
If you can help it, staying away from this highly processed food and all the additives it has can be very good for your health.
You can enjoy your favorite recipes without the fish paste and fillers by switching fake crab for a healthy protein food or one of the healthy alternatives below.
The effect of fake crab on the environment can change based on where it comes from, how it’s processed, and how sustainable the seafood industry is as a whole. Here are some considerations:
- Effects on Fisheries: Alaska pollock or other white fish are often used as the main ingredient in fake crab. It is very important that the fishery that provides these fish stays alive. The fishery can have less of an effect on the environment if it is well-run and follows sustainable practices. The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) and other certification programs can tell you if the fish used to make fake crab comes from a sustainable source.
- Bycatch: Bycatch is the unintentional capture of species that are not the target of a fishing operation. Bycatch is something that should be avoided as much as possible when fishing sustainably, and the way that imitation crab is caught can change how it affects the environment.
- Utilization of Energy: The production and processing of fake crabs require a lot of energy. This may add to the product’s environmental impact, depending on how well the process is run and what energy sources are used.
- Additives and Processing: Stabilizers, preservatives, and flavorings are some of the additives used in fake crab that may be bad for the environment. Some additives may come from natural sources, while others may be man-made. Additionally, the processing of these additives may have environmental impacts.
- Packaging: The way fake crab products are packed also has an effect on the environment. Using recyclable materials and other eco-friendly packaging methods can help reduce the damage that packaging does to the environment.
- Land Use: Agricultural methods that change land use may be used to make ingredients like starches and flavorings. Sustainable farming and sourcing can change the overall effect on the environment.
People who want to reduce the damage their food choices do to the environment can look for products that have sustainability certifications, like MSC certification for seafood. More environmentally friendly food choices can also come from buying from companies that put an emphasis on open sourcing and eco-friendly practices.
Even though it’s bad for your health, eating crab rangoon or crab cakes made from fake crab meat once in a while is usually fine. But you shouldn’t make them a regular part of your diet. There also are some people who should avoid this ingredient altogether.
Since imitation crab meat is made from fish, it is not good for vegans or vegetarians.
People with celiac disease or who are sensitive to gluten should also not eat fake crab because it contains starch and could make them sick.
If you are allergic to MSG, read the label carefully to make sure the brand you want to buy doesn’t have it. On the list of ingredients, look for words like “monosodium glutamate,” “glutamic acid,” or “glutamate.” These all mean that MSG has been added.
Additionally, some brands may use small amounts of real crab to add flavor. If you have a shellfish allergy, be sure to check the label to prevent an allergic reaction.
Surimi generally contains low levels of mercury, and imitation crab for pregnancy is likely safe in moderation. But because imitation crab has a lot of additives, it’s best to limit how much you eat and talk to your doctor before you do if you’re pregnant.
What Is Imitation Crab Meat?
Kanikama, which is another name for imitation crab meat, is often used in popular foods like crab cakes, California rolls, and crab rangoon.
So what exactly is imitation crab? Is imitation crab meat real meat?
Kani surimi, a gel-like substance made by grinding different kinds of fish into a thick paste and then adding starch, fillers, artificial flavoring, and food coloring to make it taste, feel, and look like real crab, is what fake crab is mostly made of.
Imitation crab was first produced and patented by Sugiyo, a Japanese company, in 1973. After only one year, the product started to become popular when other companies started making fake crab in the popular crab stick shape.
A few years later in 1976, Sugiyo began working with a U. S. -based company to introduce imitation crab to the United States along with the rest of the world.
Today, people all over the world eat fake crab meat, and it’s a common ingredient in many dishes.
It’s estimated that 2 million to 3 million tons of fish around the world, or about 2 percent to 3 percent of the world fisheries supply, are used to produce surimi-based products, such as imitation crab meat.
Pollock is the most common type of fish used to make fake crab meat because it is cheap, plentiful, and doesn’t taste like crab. However, cod, mackerel, and barracuda are also sometimes used.
Many people think of it as the seafood version of the hot dog because it’s low in nutrients and has a long list of additives. It’s made from fish parts and other questionable ingredients that have been ground up into a cheap, highly processed snack.
Even so, it is still used in a lot of different kinds of food because it is cheap, versatile, and easy to make.
Because it is so much cheaper than regular crab meat, it has become a popular choice for restaurants, food manufacturers, and most of all, consumers.
What Is Imitation Crab Meat Actually Made Of?
FAQ
Does imitation crab have a lot of mercury?
Is it safe to eat imitation crab meat?
Is imitation crab ok to eat while pregnant?
Is imitation crab a highly processed food?
What is imitation crab meat made of?
Imitation crab meat is made of surimi. It is a substitute for real crab meat, and essentially formed through the processing of other fish into a paste. The fish most often used is pollock. Surimi makes up about 35% to 50% of imitation crab. The rest is comprised of: ◾ Starch ◾ Water ◾ Vegetable oil ◾ Salt ◾ Egg whites or soy for protein ◾ Sugar
Does imitation crab have crabmeat?
Just like the name implies, imitation crab contains no crabmeat. Fish is, however, one of the main ingredients. It is made using surimi, which is a paste made of fish and a few other ingredients. Surimi is often made with pollock, which is also used to make fish sticks and breaded fish products. How Is Imitation Crab Made?
Is it safe to eat imitation crab?
Imitation crab, also known as ‘the hot dog of the sea’, is processed fish meat. It is commonly found in seafood salad, crab cakes, California sushi rolls, and crab rangoons. Chances are, you’ve eaten it without realizing it. In short, you can eat imitation crab.
Does imitation crab have more protein than real crab meat?
It does, but not as much as real crab meat. In comparing 3 ounces of imitation crab and real Alaska king crab, Healthline reports that imitation crab has 6.5 grams of protein compared to real crab’s 16.4 grams.
