Salmon is well known as a healthy and nutritious food, but did you know it also offers amazing benefits for your gut health? With its high content of omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients, salmon can help reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and support a healthy gut microbiome. Read on to learn more about how salmon promotes gut health and get tips for adding more of this superfood to your diet.
How Salmon Reduces Inflammation
Gut inflammation can be caused by many things, such as food allergies, long-term stress, an imbalance of gut bacteria, and digestive disorders like IBS or IBD. This inflammation triggers discomfort, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and other unwanted symptoms. There is natural pain relief in salmon because it has omega-3 fatty acids that can help reduce this pain and inflammation.
Salmon contains two key types of omega-3s: EPA and DHA. EPA and DHA have been shown in many studies to lower inflammatory markers in the body and improve the health and integrity of the gut. People with IBS, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and other inflammatory gut conditions can feel better after eating salmon because it reduces inflammation.
Regularly eating salmon and other omega-3 rich foods can help minimize flare-ups of digestive symptoms. In one study, patients with Crohn’s disease who took fish oil supplements for one year had significantly fewer relapses than those who did not take supplements
Salmon Improves Digestion
The benefits of salmon for gut health go beyond reducing inflammation. The omega-3s in salmon can also enhance digestion in several ways:
- Stimulate digestive enzymes and bile production
- Improve gut motility
- Increase absorption of nutrients
- Modulate gut microbiome
The protein and amino acids in salmon also support the stomach and intestinal lining, enabling more efficient breakdown and assimilation of nutrients from your food.
Additionally, salmon provides vitamin D, which research indicates may help prevent inflammatory bowel disease. Salmon is one of the few natural food sources of vitamin D, especially wild-caught salmon.
Salmon Supports Gut Microbiome
The complicated group of trillions of bacteria and other microbes that live in your intestines is called your gut microbiome. It is important for gut health and immune function to have a diverse and balanced microbiome.
Emerging research shows salmon can benefit your gut microbiome in a couple key ways:
-
The omega-3s help increase microbiome diversity and growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species. They also limit growth of harmful bacteria.
-
Astaxanthin, the antioxidant that gives salmon its pink color, also has prebiotic properties that feed good gut microbes.
-
Salmon protein provides amino acids that serve as metabolites for microbiome health.
More studies are still needed, but these benefits of salmon for the gut microbiome contribute to its overall support for digestive health.
Tips for Eating More Salmon
To reap the gut health benefits of salmon, aim to eat it at least twice a week. Here are some quick tips for getting more salmon in your diet:
-
Choose wild-caught Alaskan or Pacific salmon for maximum omega-3 content. Atlantic farmed salmon is a budget-friendly alternative.
-
Roast a salmon fillet and vegetable medley for an easy weeknight meal.
-
Transform leftover cooked salmon into salmon cakes, salmon salad, or salmon avocado toast.
-
Use canned salmon in place of tuna for salmon salad sandwiches or wraps.
-
Add sliced smoked salmon to salads, omelets, grain bowls, or lettuce wraps.
-
Make homemade sushi rolls with smoked or grilled salmon.
-
Whip up salmon burgers using fresh or canned salmon.
-
Stir diced grilled salmon into soups, pasta dishes, and risottos.
-
Grill a whole salmon side and use leftovers throughout the week.
With its stellar nutritional profile and versatility, there are so many great ways to enjoy salmon and reap the digestive benefits. Focus on sourcing sustainable salmon and eating it in place of less-healthy proteins like fatty beef and processed meats. Your gut will thank you!
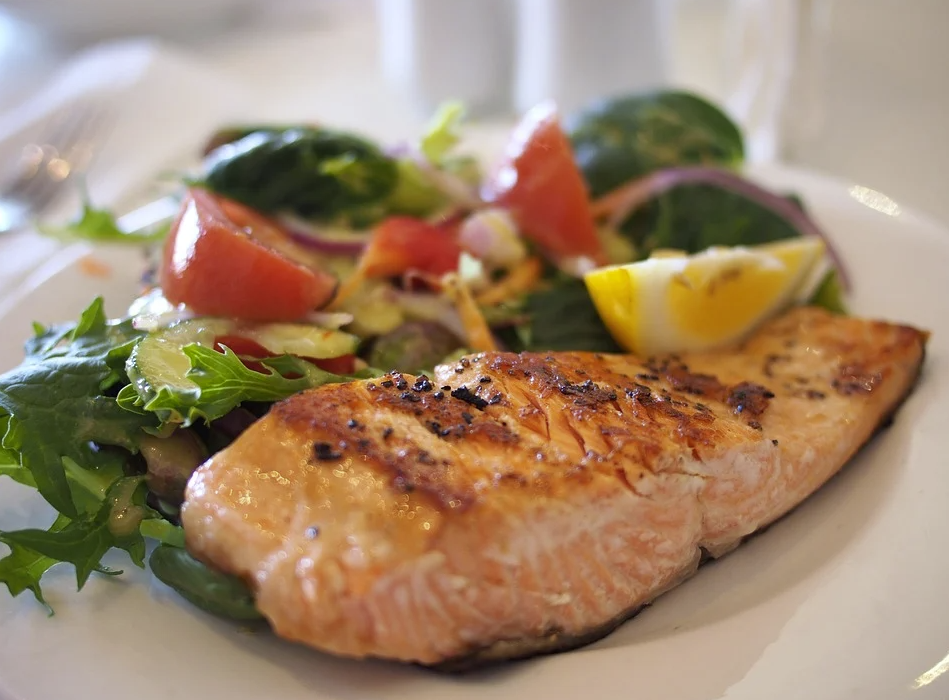
Seafood with Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to greater microbial gut diversity. They’re also thought to have a host of health benefits, like lowering inflammation, reducing symptoms of depression and improving heart health. The foods highest in omega-3s are fatty fish and some shellfish (shrimp lack omega-3s).
How much to eat: The National Institutes of Health recommends a daily intake of 1. 1 to 1. 6 grams for people 18 and over.
Probiotics are the living, good bacteria in your gut microbiome. But you can also eat probiotics in the form of “live active cultures,” which are found in naturally fermented foods like kombucha, yogurt, and kefir. Eating these foods raises the amount of probiotics in our gut microbiome, which is good for our health as a whole. It is better to eat naturally fermented foods than quick-pickled ones that get their sour flavor from vinegar.
How much to eat: Broad recommended daily intakes don’t exist, since everyone’s probiotic levels are different.
Good sources: Yogurt, miso, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, kombucha, tempeh, fish sauce Illustration by Ilka Hadlock
The Best (and Worst) Gut Health Foods
Note: The suggestions here have been reviewed by a registered dietitian nutritionist (RDN). However, they should only be used for general education and not as personalized medical care or advice. To find out what’s best for you, you should always talk to a doctor or other qualified health provider.
5 Health Benefits of Eating Salmon
FAQ
What fish is good for gut health?
Is salmon easy on your stomach?
Do eggs heal your gut?
Does salmon have benefits for skin?
Salmon is a healthy source of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and healthy omega-3 fats that make it a great fish for supporting cardiovascular health, immunity, brain function and mood, and more.
Is eating salmon beneficial?
Salmon is beneficial for health and is part of a healthy and balanced diet. Salmon has vitamin D, healthy fats, calcium, selenium, iodine, iron, phosphorus, magnesium, and protein.
Should you eat more salmon?
It’s no wonder that salmon is a staple fish (along with sardines and anchovies) in the Mediterranean diet, which is consistently considered one of the best eating plans for metabolic health and longevity. In short, Kris-Etherton concludes, “People really should, across the board, eat more seafood for overall health.”
Is salmon good for Your Heart?
Due to its combination of omega-3 fatty acids and potassium, salmon is good for your heart for a variety of reasons. Eating salmon is known to: The essential omega-3 fatty acids in salmon support scalp health and give hair its shine. On the other hand, a lack of these nutrients can result in dry scalp and dull hair.
