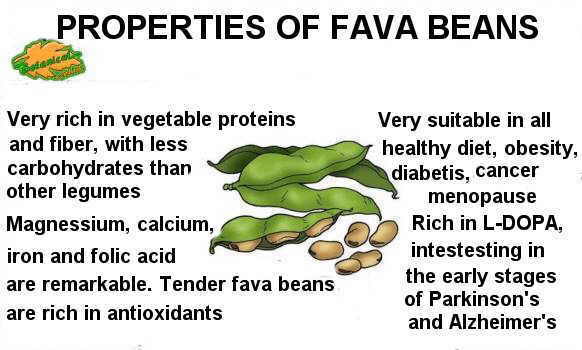
Fava beans are chock-full of nutrients and offer many health benefits. They contain fiber, folate, and manganese, among many other nutrients. Fava beans may also help decrease body weight or lower cholesterol.
They have a slightly sweet, earthy flavor and are eaten by people all over the world.
Fava beans are loaded with vitamins, minerals, fiber and protein. They’re thought to offer impressive health effects, such as improved motor function and immunity.
Fava Beans: A Surprising Natural Source of Dopamine-Boosting L-DOPA
Have you ever wondered if certain foods can boost levels of “feel-good” brain chemicals like dopamine? As it turns out, fava beans contain high amounts of L-DOPA a direct precursor to dopamine. In this article we’ll explore the science behind using fava beans as a natural dopamine booster and how to incorporate them into your diet.
What is Dopamine and Why Is It Important?
Dopamine is one of the major neurotransmitters or chemical messengers that help nerve cells communicate in the brain. Known as the “pleasure” or “reward” neurotransmitter, dopamine plays a key role in motivation, focus, learning, mood and movement control.
Low dopamine activity has been associated with depression, Parkinson’s disease, lack of motivation and addiction On the flip side, optimal dopamine levels are linked to feelings of pleasure, productivity, focus and goal achievement
Given dopamine’s importance for mental and physical health, there has been great interest in natural ways to optimize its levels. One emerging food that shows promise in this area is the fava bean.
Fava Beans Are Rich in L-DOPA
Unlike dopamine itself, L-DOPA (levodopa) can cross the protective blood-brain barrier where it gets converted into dopamine. This makes it an ideal precursor or building block for dopamine production.
Fava beans (Vicia faba) are one of the richest natural food sources of L-DOPA. A 100 gram serving contains between 2-10 grams of L-DOPA depending on the variety. That’s significantly higher than other L-DOPA containing foods like velvet beans or mucuna pruriens.
In fact, fava beans have the highest concentration of L-DOPA of any natural food source. This gave rise to their study as a potential natural treatment for dopamine-related disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
Studies on Fava Beans and Dopamine
Several studies have hinted at the dopamine-boosting potential of fava beans:
-
A 2015 study in Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery found increased urinary dopamine levels in healthy individuals after consuming fava beans. This suggests the bean’s L-DOPA content is effectively converted into dopamine in the body.
-
In 1993, researchers in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry found Parkinson’s disease patients who ate fava beans experienced improved motor function comparable to dopamine medication, although benefits were short-lived.
-
An older study in the European Neurology Journal in 1987 also found significantly increased dopamine metabolites in Parkinson’s disease patients after eating fava beans.
While promising, it’s important to note that using fava beans to boost dopamine has variable effects and should not replace medical treatment. However, as part of a dopamine-promoting lifestyle, they may provide benefits.
Other Ways Fava Beans Support Brain Health
Beyond L-DOPA, fava beans contain a host of other brain-boosting nutrients:
-
Protein and amino acids for focus, mood and neurotransmitter synthesis.
-
Prebiotic fiber to nourish good gut bacteria linked to mental health.
-
B vitamins like folate, thiamine and pantothenic acid required for energy production and cognitive function.
-
Minerals including iron, zinc, manganese, magnesium and copper which play roles in neural conduction and neurotransmitter balance.
This unique nutritional profile gives fava beans the ability to support brain health on multiple levels.
How to Add Fava Beans to Your Diet
If you want to harness the natural L-DOPA in fava beans, the good news is they are widely available and easy to prepare. Canned fava beans offer convenience while dried beans provide cost savings and more flavor. Some tips:
-
Look for young, medium-sized beans which tend to be milder in taste. Larger, mature beans can be bitter.
-
Soak dried beans overnight then simmer until tender – about 45 minutes to an hour. Canned beans only require rinsing.
-
Fava beans have a nutty, sweet flavor similar to edamame or peas. They work well in soups, curries, salads, hummus, pasta and rice dishes.
-
Try adding fava bean flour to smoothies, baked goods or nutrition bars for an extra nutrition and dopamine boost.
-
Roast fava beans with olive oil, salt and spices for a crunchy, dopamine-rich snack.
For optimal effects, nutritionists recommend eating 1/2 to 1 cup of fava beans two to three times per week. Introduce them slowly to assess tolerance.
Potential Side Effects of Fava Beans
Fava beans are considered safe for most people but there are some precautions:
-
Fava beans contain vicine, a compound that can trigger hemolytic anemia in those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency.
-
They contain dopamine precursor L-DOPA which may interact with MAO inhibitors and other medications. Those on medication should consult their doctor before eating large amounts.
-
Some people report digestive issues like gas, bloating and stomach pain after eating fava beans, especially in large quantities. Introduce them gradually.
-
Fava beans may trigger allergic reactions in those with legume allergies. Discontinue use if any signs of food allergy appear.
As with any dietary change aimed at improving health, it’s wise to start slowly and monitor your response. Discuss any concerns with your healthcare practitioner.
A Holistic Approach to Naturally Boosting Dopamine
While fava beans show promise for raising dopamine levels, they are just one piece of the lifestyle puzzle for optimal brain health. Here are some other evidence-based ways to increase dopamine naturally:
-
Exercise – Works both short and long-term to increase dopamine receptors and availability.
-
Get enough sleep – Lack of sleep reduces dopamine signaling.
-
Reduce stress – High stress depletes dopamine over time.
-
Listen to music – Releases a flood of feel-good dopamine.
-
Get some sun – Increases vitamin D which regulates dopamine.
-
Try dopamine-boosting supplements like mucuna pruriens, vitamin D, omega-3s.
-
Eat prebiotic foods – Support gut microbes that influence dopamine levels.
The best approach is to combine dopamine-friendly foods like fava beans with these other lifestyle habits for maximum brain benefits.
The Bottom Line
Current research indicates fava beans may naturally boost dopamine levels thanks to their uniquely high L-DOPA content. Introducing fava beans into a balanced, dopamine-promoting diet and lifestyle can offer brain-boosting benefits. However, effects can vary individually and fava beans should not replace medical treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before making significant diet changes, especially if you have a medical condition.
References:
May Improve High Blood Pressure
Fava beans are high in nutrients that can improve heart health.
In particular, they contain magnesium and potassium that may relax blood vessels and prevent high blood pressure (31).
It has been shown in several studies that the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet, which suggests eating foods that are high in potassium and magnesium, can help lower high blood pressure (32, 33, 34).
In addition, a 10-year study in 28,349 women found that those with the highest dietary intake of magnesium were less likely to develop high blood pressure than those with lower intakes of this mineral (35).
Based on this study, eating fava beans and other magnesium and potassium-rich foods may help lower blood pressure and keep the heart healthy.
Loaded With Nutrients
For their relatively small size, fava beans pack an incredible amount of nutrients.
In particular, they’re rich in plant protein, folate and several other vitamins and minerals. They’re also loaded with soluble fiber that can aid digestion and lower cholesterol levels (1, 2).
One cup (170 grams) of cooked fava beans has (3):
- Calories: 187 calories
- Carbs: 33 grams
- Fat: Less than 1 gram
- Protein: 13 grams
- Fiber: 9 grams
- Folate: 40% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Manganese: 36% of the DV
- Copper: 22% of the DV
- Phosphorous: 21% of the DV
- Magnesium: 18% of the DV
- Iron: 14% of the DV
- Potassium: 13% of the DV
- Thiamine (vitamin B1) and Zinc: 11% of the DV
In addition, fava beans provide smaller amounts of almost all other B vitamins, calcium and selenium.
Treating Parkinson’s Disease with Fava Beans (Faba or Broad Beans)
FAQ
Do fava beans increase dopamine?
Which beans increase dopamine?
What are fava beans high in?
Who should not eat fava beans?
Are fava beans a dopamine?
Fava beans contain 0.5% L-DOPA (0.07% when dried) [ 1 ]. It was Vicia faba from which L-DOPA was first isolated by Guggenheim in 1913, while the discovery of the enzyme DOPA decarboxylase by Holtz in 1938 revealed that L-DOPA is the precursor of dopamine [ 36 ].
What vitamins, minerals, and supplements can help increase dopamine levels in the body?
Although there are many claims for supplements that increase dopamine levels, there is no scientific evidence to clearly support any of them. However, there are natural ways to boost dopamine activity in the brain, including exercise (especially outdoors), getting enough good quality sleep, and meditation.
Do fava beans increase L-DOPA levels?
Fava beans (Vicia faba) have a high phenolic content and fava bean consumption can increase the levels of L-dopa in the blood, with a marked improvement in the motor performance of the patients, without any side effects [ 5 – 7 ]. The primary motor complications of the levodopa therapy are fluctuations and dyskinesias [ 1 ].
Do fava beans contain levodopa?
Fava beans contain levodopa, the same chemical in Sinemet, Madopar, Dopar, Larodopa, and other levodopa-containing medicines used to treat PD. In fact, the entire fava plant, including leaves, stems, pods, and immature beans, contains levodopa.
