Cocoa beans have a long and fascinating history They originate from the Theobroma cacao tree, which is native to South America. Today, cocoa beans are grown around the world in the tropical regions near the equator.
The Origins of Cocoa in South America
The Theobroma cacao tree originated in the upper Amazon basin region of South America primarily in parts of present-day Brazil Colombia, and Peru. Cacao trees thrive in hot, rainy environments in the tropical regions within 20 degrees latitude of the equator.
Archaeological evidence shows that cacao was first cultivated and consumed by pre-Columbian cultures in South America as early as 1900 BC. The oldest known cultivation site is Santa Ana-La Florida in Ecuador, where the Mayo-Chinchipe people grew cacao trees over 5,000 years ago.
Cacao was highly prized by indigenous cultures such as the Maya, Aztec, and Olmec civilizations. The cacao beans were used to make chocolate drinks for religious rituals and as currency for trading. The beans were introduced to Central America around 400 AD and spread as a commercial crop throughout Mesoamerica.
Cacao Comes to Africa and Asia
After European colonization beginning in the 16th century, cacao cultivation spread from South America to equatorial regions around the world. Spanish and Portuguese colonists established cacao plantations in the Caribbean, Philippines and West Africa.
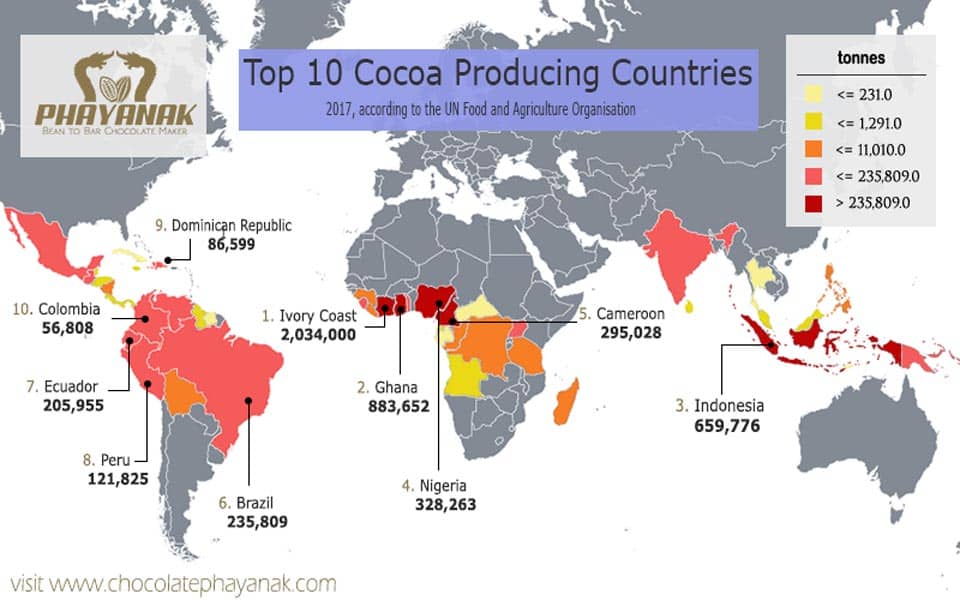
Today, over 70% of the world’s cocoa beans are grown in a belt along the southern coast of West Africa. The climate in countries like Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Nigeria and Cameroon is ideal for cacao trees. West Africa produces over 3 million tonnes of cocoa beans per year.
Cacao was also brought to tropical areas of Asia in the 17th-19th centuries by Europeans. Indonesia is now the third largest cocoa producer in the world after Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana, with an annual crop of over 730,000 tonnes of beans. Other countries in Southeast Asia with significant cocoa production include Malaysia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines.
Cocoa Bean Production Spreads Around the Tropics
While West Africa and Asia remain the leading cocoa producing regions, many other tropical countries around the world also grow cacao trees. In the Americas, cocoa is an important commercial crop in Brazil, Ecuador, Colombia, Dominican Republic and Mexico. Some Caribbean islands such as Jamaica and Trinidad also produce cocoa.
In Africa, other cocoa producers include Nigeria, Cameroon, Sierra Leone, Uganda and Tanzania. Cocoa farming was introduced to East Africa in the early 20th century by German colonists.
There are small but growing cocoa industries in tropical countries like Vietnam, Fiji, India, Sri Lanka and Madagascar. Better farming practices and disease-resistant cacao varieties have allowed cocoa production to expand within 20 degrees of the equator.
Over 50 Countries Produce Cocoa Today
While the Theobroma cacao tree originated in South America, today over 50 countries around the equatorial belt grow cocoa commercially. Millions of smallholder farmers and plantations collectively produce over 4.5 million tonnes of cocoa beans each year.
The top 5 cocoa producing countries are Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Indonesia, Nigeria and Cameroon. But many more countries contribute to the global cocoa supply, including Brazil, Ecuador, Malaysia, Dominican Republic, Peru, Colombia, Papua New Guinea, Uganda, Mexico and the Philippines.
Most cocoa farms are located within 8 degrees north or south of the equator and rely on the hot, rainy climate for good harvests. Due to increasing demand for chocolate worldwide, cocoa bean production continues to expand into suitable equatorial regions across Asia, Africa, Oceania and the Americas.
So while cocoa originated in South America, today it is very much a global commodity grown across the tropics and exported around the world to make chocolate. The ancient bean once prized by pre-Columbian cultures is now enjoyed worldwide thanks to cocoa’s spread across the equatorial regions.
How to use cocoa beans
Cocoa beans are the starting point for all chocolate production. You can use the beans to make you own dark or milk chocolate bars. Another thing is that you can eat cocoa beans raw like nuts if you like strong, complex bitter tastes.
They retain all their nutrients this way, as they are uncooked and unprocessed. Raw beans are packed with health benefits, as we will see shortly. Remember, though, that these beans are very bitter and can’t be used instead of dark chocolate.
The cocoa beans are taken out of their shells and ground into small pieces, or nibs, after being roasted to bring out all of their cocoa flavors.
Professionals are using cocoa nibs more and more in their recipes. They give desserts a unique texture. They also have a very intense cocoa flavor. Their bitter notes are much sought-after for the unique taste they provide. They are ideal for flavoring recipes and adding taste and texture. Nibs work wonderfully in cakes, ganaches, ice creams and even chocolate bars.
Where do cocoa beans come from?
Cocoa pods grow on cacao trees (Theobroma cacao). This small tree of Mexican origin blossoms all year round. It has pink and white flowers, but only a few will turn into fruit—about one in every 500.
Theobroma cacao grows pods on both its branches and trunk. Growers have to be very careful not to damage the cacao tree when harvesting them. Because it’s such a delicate task, pods are picked by hand.
Each bean is made of about 50% of a fat called cocoa butter. The beans are mostly protein and water, and they also have a lot of nutrients like theobromine and vitamins. The beans also contain starch and other minerals.
Each pod contains 16 to 60 cocoa beans. You have to extract the fruit’s contents to get at its beans, in a process known as de-seeding.
When fresh, beans look like seeds covered in a white, sticky pulp called mucilage. They can be eaten as they are. However, if we want to store them for later use, we have to ferment and then dry them. We can also roast them.
How It’s Made: Cocoa Beans
FAQ
Where did cocoa beans originate?
Is cocoa a fruit or nut?
Is cocoa bean a tree or bush?
Who brought cocoa to America?
Where do cacao beans come from?
Cocoa beans in the fruit of the cacao tree (Theobroma cacao), the source of cocoa and chocolate. The plant is native to tropical regions of Central and South America but is primarily cultivated in western Africa. After four years a mature cacao tree produces fruit in the form of elongated pods that range in colour from bright yellow to deep purple.
What is the history of cocoa bean?
The cocoa bean’s legacy is deeply intertwined with the history of our planet. Its journey began in the tropical rainforests of Mesoamerica, where the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs revered it as a divine gift. They cultivated it, using its seeds not only for food but also for religious ceremonies and as a form of currency.
What is a cocoa bean?
The cocoa bean, also known simply as cocoa ( / ˈkoʊ.koʊ /) or cacao ( / kəˈkaʊ / ), [ 1] is the dried and fully fermented seed of Theobroma cacao, the cacao tree, from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances) and cocoa butter (the fat) can be extracted. Cacao trees are native to the Amazon rainforest.
Where did cacao come from?
Cacao was consumed by pre-Hispanic cultures in spiritual ceremonies and its beans were a common currency in Mesoamerica. The cacao tree grows in a limited geographical zone; today, West Africa produces nearly 81% of the world’s crop. The three main varieties of cocoa plant are Forastero, Criollo, and Trinitario; Forastero is the most widely used.


